 Perma-Chink Systems, Inc
Log & Timber Home Care Experts
Perma-Chink Systems, Inc
Log & Timber Home Care Experts
The Dynamics of Weathering for Round Logs, Square Logs and Log Siding

Many people are under the impression that the winter months are hard on their logs and finishes. To some extent that’s true. In cold climates where the exterior log surfaces may be covered with ice and snow for several months can be damaging if the logs aren’t properly finished. But even then, the most damaging effects of weather on wood and coatings actually occur during the hot summer months. Once homeowners understand the main causes of surface weathering, the better equipped they will be in choosing the right products to protect the home from weathering.
Understanding The Causes of Weathering
One component of sunlight is ultraviolet light, commonly referred to as UV light, or UV rays. UV light is responsible for most damage to exposed wood because it changes or destroys the wood’s lignin, a component of wood that hardens and strengthens the cell walls. In more scientific terms, this process is called photo-oxidation.
Lifeline™ finish systems help retard this photo-oxidation process through three distinct mechanisms: reflection, absorption, and chemical reaction. Our Advance Gloss and Advance Satin topcoats help reflect the sun’s rays, thus reducing the amount of UV light hitting the color coats and the underlying wood.
Glossy surfaces are better reflectors than dull surfaces, which is why our Advance Gloss provides a bit more protection than Advance Satin. However, an accumulation of dirt on the finish will significantly reduce the reflective properties of the topcoat, one reason why a home should be routinely cleaned with Log Wash™. Advance topcoats also help protect the color coats and wood from the abrading effects of wind, rain, ice, and snow.
The profile of the logs has a significant impact on the weathering characteristics of a wall. The effect of sunlight and the weather on round logs is altogether different than on square logs or flat, vertical siding.
ROUND LOGS 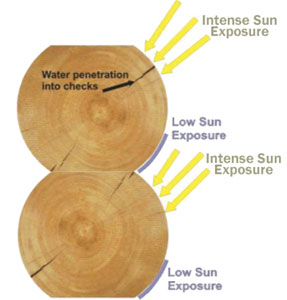
The top third of a round log is subjected to much more intense weathering than the bottom third. In cold weather climates snow and ice can accumulate on the upper third while the bottom third remains somewhat protected. Upward facing checks that have formed in the top section of the log will funnel rainwater directly into the interior of the log where it can soak into the surrounding wood. But most damaging of all is the angle of the top third of a round log towards the sun. The top third of round logs catches many times more UV light than the bottom third. Besides exposing the wood to more UV exposure, the UV inhibitors in the upper third may become used up, whereas in the lower third they may still be active. Over time this can result in a noticeable difference in color and signs of weathering between the upper and lower sections of the logs. Providing some maintenance to the upper sections of round logs without creating lap marks or color differences can be accomplished, but it may be a bit of a challenge. The key is to do the maintenance before the wood becomes gray due to photo-oxidation.
SQUARED LOGS
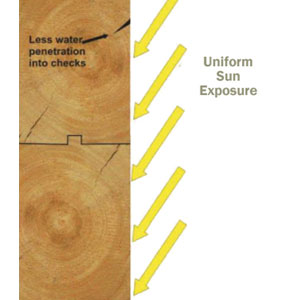 Squared logs and vertical flat siding are easier to maintain since the sun hits the logs at the same angle, and the UV light is evenly distributed over the entire surface. In addition, the flat vertical surfaces cannot accumulate snow and ice and even upward facing checks are not as prone to rainwater entering the logs. Although squared logs are subject to the same weathering parameters as round logs, and since the weathering is mostly uniform over the entire exposed surface, maintenance is easier to accomplish without worrying about lap marks and color differentiation.
Squared logs and vertical flat siding are easier to maintain since the sun hits the logs at the same angle, and the UV light is evenly distributed over the entire surface. In addition, the flat vertical surfaces cannot accumulate snow and ice and even upward facing checks are not as prone to rainwater entering the logs. Although squared logs are subject to the same weathering parameters as round logs, and since the weathering is mostly uniform over the entire exposed surface, maintenance is easier to accomplish without worrying about lap marks and color differentiation.
LOG SIDING
Round log siding probably presents the greatest challenge to forestalling the effects of weathering. Typically used in high exposure locations such as dormers and gable ends, in addition to suffering the same weathering characteristics as round logs, log siding has some features which makes it even more difficult to protect from the effects of the weather. Siding is often manufactured from lower quality wood than logs, frequently using green wood. This makes it more susceptible to twisting, warping and cracking. Since siding does not have the high thermal mass of full logs, during the summer months their temperature can range from 80ºF to 160ºF - or higher - during the course of one day. This puts a lot of mechanical stress on both the siding and its finish system resulting in small fissures forming on the surface. Rainwater can then enter these fissures and get behind the finish.
FISSURING OF LOG SIDING
Round log siding is typically milled quite smooth. The extreme smoothness presents a challenge applying the proper thickness of pigmented film necessary for adequate protection of the underlying wood. Smooth log siding should be coarse sanded or pressure washed using Wood ReNew™ before the application of the pigmented stain.
Protect From Weathering
There are two basic ways to combat the effects of weathering. The most effective method is to keep log walls and siding in the shade by extending roof overhangs or constructing roofed porches around the home. In conjunction with using a high quality finish system like Lifeline™ Ultra-7 and Advance Topcoat, this will be the most effective measure to prevent excessive weathering. If unable to protect by structural shade, the next best way is to apply the best finish system - Lifeline™ Ultra-7 and Advance Topcoat. But the overall performance of even the best finish system is dependent upon proper surface preparation and application technique. Avoiding the use of chlorine bleach will preserve the wood and finish, and back-brushing all coats of finish to assure adequate film thickness is crucial for long-term protection of the wood.